Joins
- PostgreSQL supports
- inner join,
- left join,
- right join,
- full outer join,
- cross join,
- natural join,
- and a special kind of join called self-join.
basket_a
a | fruit_a
---+----------
1 | Apple
2 | Orange
3 | Banana
4 | Cucumber
(4 rows)
basket_b
b | fruit_b
---+------------
1 | Orange
2 | Apple
3 | Watermelon
4 | Pear
(4 rows)
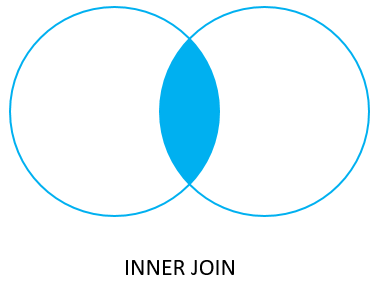
Inner Join
-
Returns the rows whose values are equal based on the "ON" condition.
-
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
INNER JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+---------+---+---------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
(2 rows)
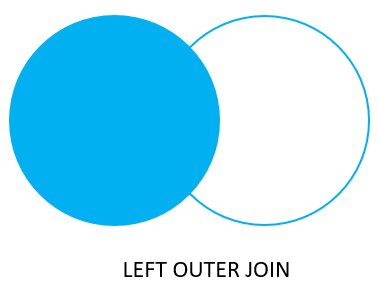
Left Join / Left Outer Join
-
Returns the rows which are present in left table but not in right table (except common rows).
-
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
LEFT JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+----------+---+---------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
3 | Banana | |
4 | Cucumber | |
(4 rows)
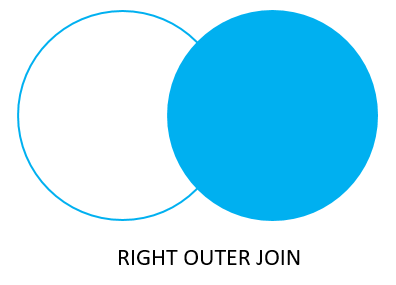
Right Join / Right Outer Join
-
Returns the rows from right table which are not present in left table (except common rows).
-
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
RIGHT JOIN basket_b ON fruit_a = fruit_b;
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+---------+---+------------
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
| | 3 | Watermelon
| | 4 | Pear
(4 rows)
Full Outer Join
-
Returns rows from both left and right table.
-

SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
FULL OUTER JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+----------+---+------------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
3 | Banana | |
4 | Cucumber | |
| | 3 | Watermelon
| | 4 | Pear
(6 rows)
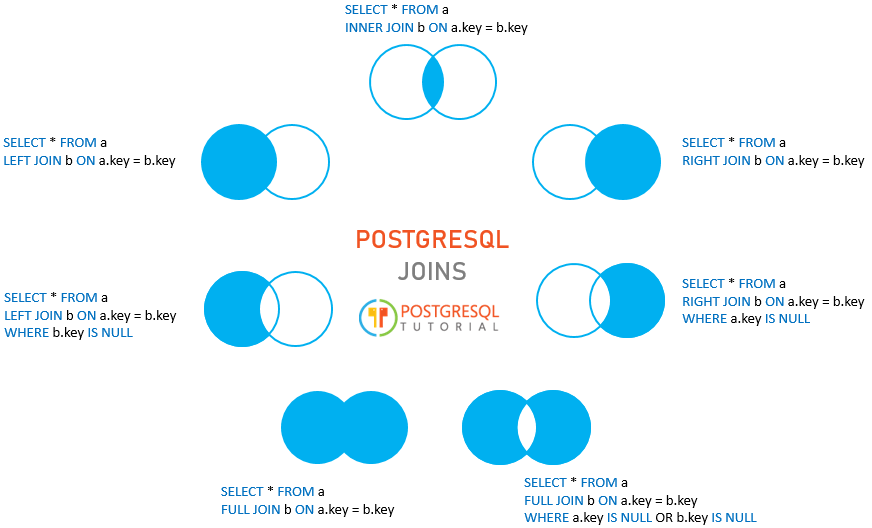
Table Aliases
SELECT
c.customer_id,
first_name,
amount,
payment_date
FROM
customer c
INNER JOIN payment p
ON p.customer_id = c.customer_id
ORDER BY
payment_date DESC;
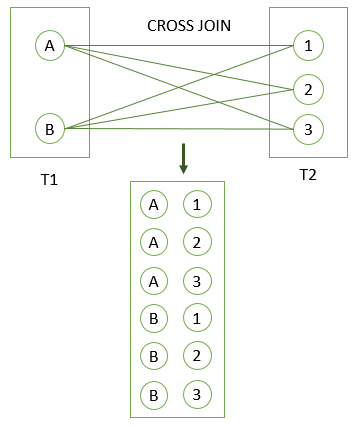
Cross Join
-
A CROSS JOIN clause allows you to produce a Cartesian Product of rows in two or more tables.
-
Different from other join clauses such as LEFT JOIN or INNER JOIN, the CROSS JOIN clause does not have a join predicate.
SELECT select_list
FROM T1
CROSS JOIN T2;
Natural Join
-
A natural join is a join that creates an implicit join based on the same column names in the joined tables.
-
A natural join can be an inner join, left join, or right join. If you do not specify a join explicitly e.g., INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, PostgreSQL will use the INNER JOIN by default.
SELECT * FROM products
NATURAL JOIN categories;
is same as
SELECT * FROM products
INNER JOIN categories USING (category_id);